SEO Audits Explained – What is an SEO Audit?
Table of Contents
Many SEO experts can neglect the initial foundation and planning phase of a client’s SEO strategy and performance.
In modern data search engine optimization, it is more than just keyword rankings – it is about capturing your target audience and ensuring that your searchers get what they need from your content.
Your product or article should solve a problem. When optimizing a website, consider a user’s typical pain point within your niche and conduct your optimization with that in mind.
Solving a problem will boost your return on SEO investment and provide a great user experience that keeps people coming back to your website.
This why it is essential to conduct a full and extensive SEO and website audit on the website PRIOR to any work being done.
Article highlights:
- Understand an SEO audit and what it should achieve
- How to approach an audit
- Essential tools to use for the audit process
- Best areas to cover in an audit
- Free Technical SEO audit Checklist with actionable points
What is an SEO audit?
An SEO audit is an in-depth analysis of a website’s inner workings, structure, accessibility to search engines, and ability to perform well in a digital marketing-driven driven world.
Google has to be able to access, crawl and show your websites to your audience for your audience to engage your website. For this process to happen, many tick boxes need to be checked from a search engine perspective.
These ‘tick boxes’ are what we aim to analyze in an audit and identify ways to improve them to improve the overall website performance.
What is a Content Audit?
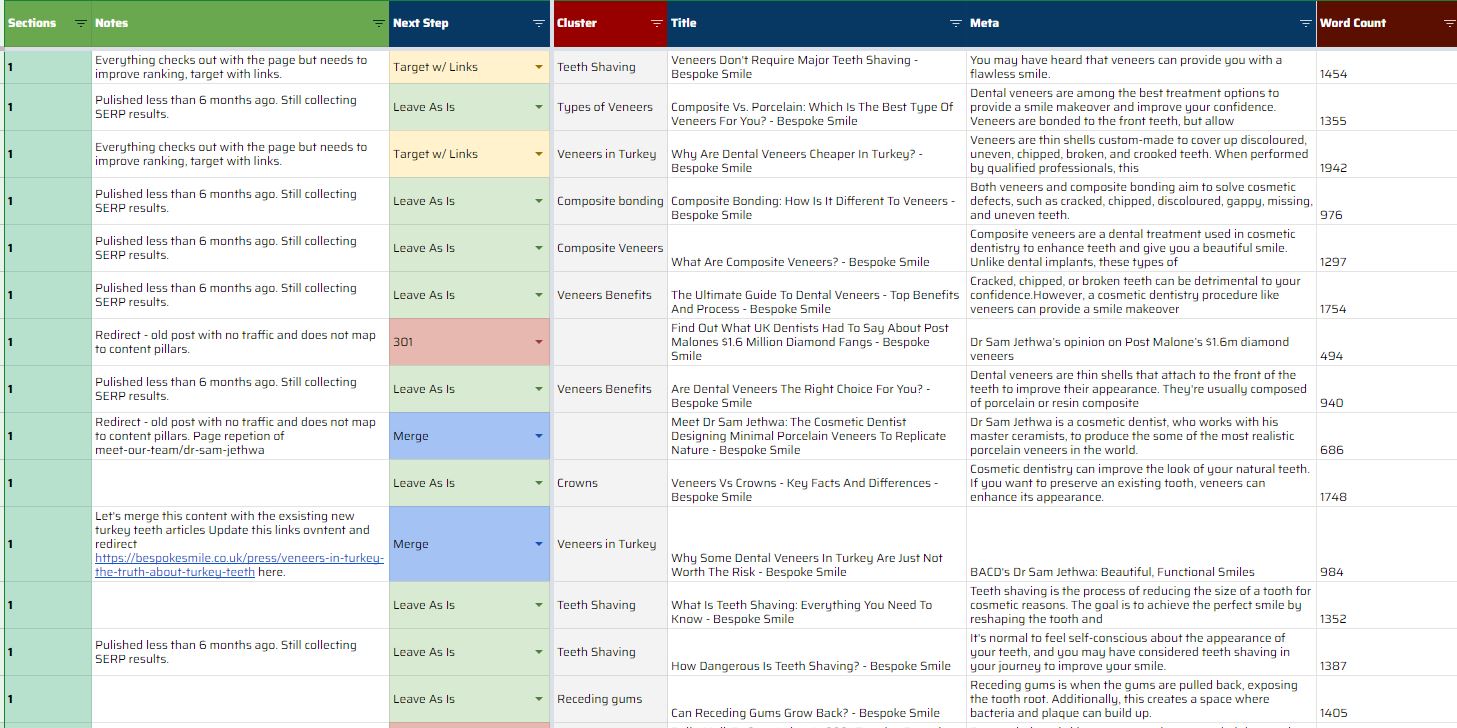
A content audit will follow a similar process to an SEO audit and many agencies will analyze a website’s content when conducting the SEO audit process.
Despite this being a good approach, an in-depth content audit is actually a separate deliverable that should be conducted as its own standalone analysis.
The core difference is that when auditing website content, you will spend quality time focusing on the analytics data, user engagement, and rankings of a specific page.
Within this process, you will also analyze the target keywords of a page and ensure that the content on the webpage is targeting the correct user intent for the primary keyword.
It will not involve assessing any technical aspects of a page, that is handled within the SEO audit itself.
Explain how a content audit can act as a guide for your content team, which can result in ranking higher in SERPs.
In a few sentences, outline the difference between an SEO audit and a content audit as many people confuse the 2 and often believe they are the same thing.
Google’s crawlers need to see that the relevance of a page is targeting the intent of the keyword and this will help increase visibility in the search engine results.
5 Essential Audit Steps And What They Mean
Follow these guidelines to cover the top 5 essential elements of a site audit and start to see quick wins and improved click-through rates!
1: Only One Version of your Site Should Exist (Canonical)
What is meant by canonical URL? According to Google, a canonical URL is the URL of the best representative page from a group of duplicate pages. However, let’s start by checking the canonical (original) version of the domain itself.
When a domain is registered, multiple versions of that website become available. One version with HTTP and one version with HTTPS. One version includes the ‘www’ and one version which doesn’t for example:
- http://yourdomain.com
- http://www.yourdomain.com
- https://yourdomain.com
- https://www.yourdomain.com
To avoid duplicate content and crawl errors, only one version of your website should exist. Choose one version of the domain (I usually go with https://yourdomain.com) and permanently 301 redirect the rest of the domains to this one main version.
Here is the HTTP version of our website which will 301 redirect to the HTTPS version.
Add image https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Pcf4Hj2BAxyikfwqG-WAtvaEZ6IoB9B0/view?usp=sharing
Add image https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EN7WyMVZeQtdI7ypHOseC1YfNFt1JsEy/view?usp=sharing
A handy way of checking the status of canonical versions of a page is by using the Ahrefs toolbar which will show you the status of the redirect (if any) once clicking on the ‘HTTP Headers 301’.
A handy way of checking the status of canonical versions of a page is by using the Ahrefs toolbar which will show you the status of the redirect (if any) once clicking on the ‘HTTP Headers 301’.
2: Look for Indexation Issues
Indexing is the process of Google accessing and crawling your website, understanding the content and topical elements, and making it available in their index.
To summarize the indexing process, Google will visit the page by the Google crawler (“Googlebot”), analyze content and internal links meaning, and then store your content in the Google index.
Read this great article from Moz about how search engines work. Indexation problems can be caused by many different factors which we will address below, however, it can be very common amongst any type of website.
However, large E-commerce sites are often a victim of indexation issues simply due to the number of products and associated sections.
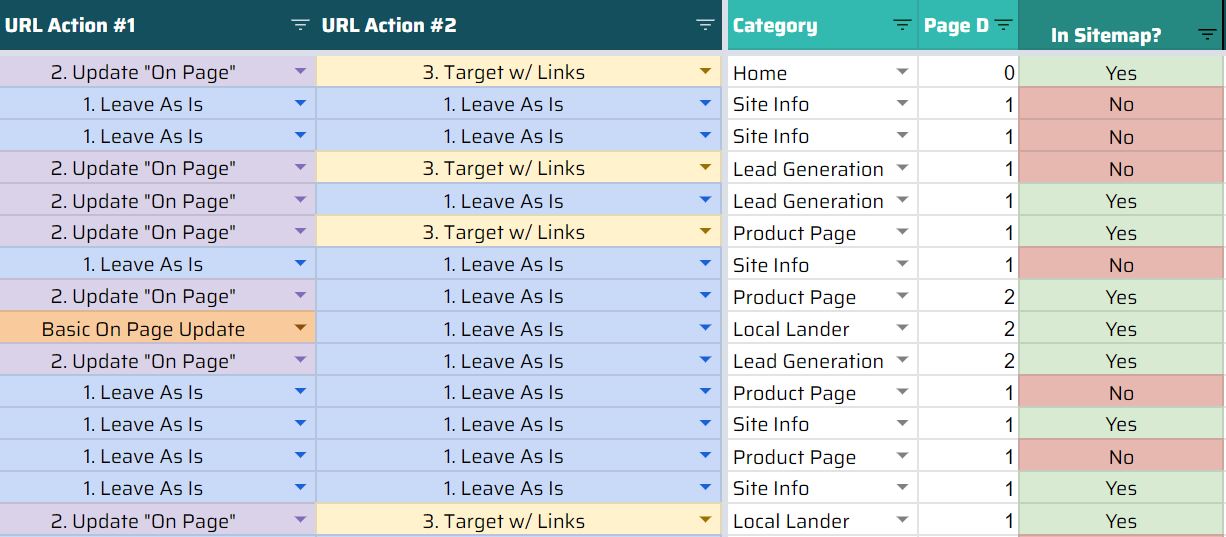
Let us look at a real example of a site we recently audited:
An E-commerce clothing store had a total of 2683 indexable HTML pages as per a crawl in Screaming Frog, however, when searching for the domain-specific pages in Google, only 599 pages were indexed.
In this particular case, there were many sections of the website which were incorrectly blocked in the robots.txt file and there was an issue within the XML sitemap.
Analyzing the Robots file and XML Sitemaps
To continue with the above issue, it is essential to view both the robots.txt file and all existing XML sitemaps.
Your robots.txt file will inform search engine crawlers which URLs the crawler can access on your site and which they can not. Any web developer or webmaster should understand the use of a robot’s file and what to avoid.
The robots file is extremely useful if used correctly in the following ways:
- Block any specific sections of your website or any specific landing pages
- If needed, media files can be blocked from appearing in Google search results without negatively impacting your site’s SEO
- Unimportant external scripts and resource files can be blocked
3 ways your robots file can be dangerous if used incorrectly:
- The website is set to no-index
- Robots.txt not added into the root directory of your site
- No XML Sitemap URL listed in the file (I recommend adding all of your relevant XML sitemaps in your robots file
Another crucial part of crawling and indexing your website is your XML file. If configured and working correctly, Google will be able to crawl your website quickly and effectively which leads to better results in organic search.
The XML sitemap is a specific file that compiles a whole list of the website’s important pages, making sure Google can find and crawl them all. It also helps search engines understand your website structure and build a hierarchy around the structure of your content.
All of the popular SEO plugins out there will automatically create a sitemap for you, however, you will still need to check each sitemap to validate the number of pages within each folder and if all the pages are relevant.
You are also able to view any issues with your sitemaps in Google Search Console:
If you are using Screaming Frog or the Ahrefs site audit tool, you will easily be able to see if there are any broken pages or broken links within your XML sitemaps.
This is what a typical XML sitemap will look like (image courtesy of Yoast SEO)
3: Don’t Forget the Basics of On-Page SEO and Meta Tags
On-page SEO is so often overlooked and many sites lose out on quality traffic due to low organic click-through rates.
I am not only talking about just title and meta descriptions (these are also essential), but I am also talking about the effective use of secondary and semantic keywords, internal links, image size, image ALT text, anchor text as well as relevant markup needed for each type of page on your site.
For anyone who may think that on-page metrics (especially the title and description tags) do not play a huge role in organic traffic, just take a look at this graph based on a study that Search Engine Land completed:
When auditing a site take a look at what the current title and description tags are, the status of h1 headings, and word count too.
You can easily see this data in Screaming Frog by navigating to ‘page titles’ and scrolling through the menu to find any pages missing title tags or any which need to be redone.
You can also view the results of a site audit run through the Ahrefs site auditor tool. I like the visual aspect of their audit reports and it is also easy to access the data which needs fixing.
Using the correct structured data on your content is essential to help search engines understand your content in a more in-depth manner.
Structured data (aka schema mark-up) is a standardized method of providing core information about a page and classifying the page content. Every single page on a website needs to have structured data about the type of service or category the page is talking about.
For example, here is the correct structured data code for a recipe page, what are the ingredients, the cooking time and temperature, the calories etc.
<html>
<head>
<title>Party Coffee Cake</title>
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org/”,
“@type”: “Recipe”,
“name”: “Party Coffee Cake”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “Mary Stone”
},
“datePublished”: “2018-03-10”,
“description”: “This coffee cake is awesome and perfect for parties.”,
“prepTime”: “PT20M”
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Party coffee cake recipe</h2>
<p>
<i>by Mary Stone, 2018-03-10</i>
</p>
<p>
This coffee cake is awesome and perfect for parties.
</p>
<p>
Preparation time: 20 minutes
</p>
</body>
</html>
Again, most popular SEO crawlers will identify errors in structured data, but here is an easy way to find these elements in Screaming Frog. Just navigate to the ‘structured data’ section and view the results.
You can toggle through the drop-down menu options which will show you which pages have structured data, which pages don’t, or if there are any errors with the structured data.
Alternatively, you can use the official Google rich snippets tester here and test on a page level. However, keep in mind that this will only test one URL at a time, so a bulk checker SEO tool will be easier to use at scale.
4: Page Speed and Core Web Vitals Testing
Possibly one of the most crucial aspects to your website SEO is site speed, mobile-friendliness as well as core web vitals (Page Experience).
Before we address page speed (the faster the load time the better for user experience and google), we need to understand a little bit more about the official Page Experience update.
According to this article by Search Engine Journal, the page experience update considers several signals that go into creating an optimal experience for users.
Google assesses each of the signals and gives a website an overall ‘page experience’ score.
Generally speaking, you want to give your website users and online customers the best possible experience, and so does Google.
Google Search Console has a whole section dedicated to Page Experience and allows you to view the core web vitals performance of each page and make the needed tweaks from there.
An extremely handy tool to check page-level load time results on both mobile and desktop is the official Google page speed insights test which will also provide you with opportunities for improvement.
Sidenote: I have found that when presenting audit findings to a client or business owner, using easy-to-understand and highly visual images works best.
This is also where the Page Speed Insights tool will come in handy, as you can add a few screenshots of the test and then write down or talk about the suggestions to improve.
For example, adding these into a client document with some valuable points to address is a powerful way to grab attention.
However, with the Page Speed Insights tool, you can only test one page at a time. It is useful to test a few core pages (one after the other) but, or a better view of a website’s technical audit status, then you need something which can access these metrics at scale.
You can integrate the Google Page Speed Insights API into Screaming Frog and gather the speed metrics for every page in one crawl.
This function is awesome, but it does take a bit of extra time to crawl depending on the size of the website.
Here is an overview of how to enable the Page Speed API and run the crawl through Screaming frog. However, I do recommend reading their step-by-step guide on how to generate the API.
How to integrate the PSI API into Screaming Frog (overview)
Step 1: Click on the ‘API’ tab at the top right-hand side of the control panel and it will show you a list of APIs available.
Step 2: Navigate to the Page Speed Insights column and click on the gear icon.
Step 3: A window will appear which will require you to paste in your ‘secret key’ (obtained by following the link to the guide above).
Step 4: Add your secret key and click on connect.
5: Link profile Analysis and Link Building Overview
Very often we come across websites that experience traffic drops for no obvious reason which is why technical SEO audits need to cover a variety of aspects.
In this article, we have just addressed 5 of the core aspects of an audit which offer powerful insights into quick wins.
But if you would like to dive deeper and address a wider set of technical parameters, then download this extensive technical SEO scorecard for free (just make a copy to be able to use it).
The final step I would like to cover about auditing is around your website’s backlink profile. Too many SEO agencies or consultants shy away from addressing link building as it can be a gray area or one which they feel can be hard to justify to a client.
However, keep in mind that quality backlinks and mentions from quality, relevant third-party websites are still a huge part of Google’s ranking factors. View how we do link building.
My favorite tool for anything to do with Backlinks is Ahrefs (shout out to Tim Soulo and Sam Oh.
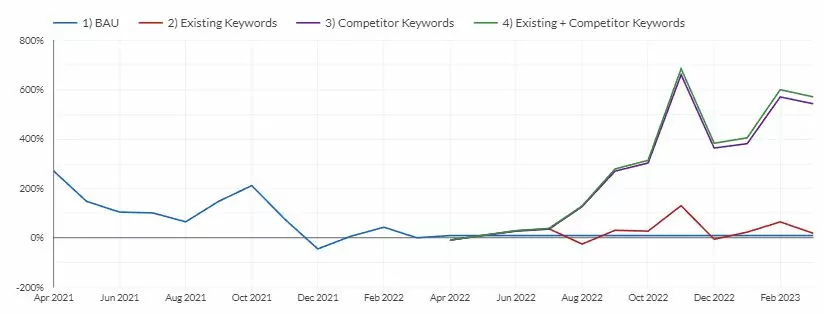
Start by running the target website through the Ahrefs site explorer tool, select all time, then one year, and then 30 days and look for anything which stands out to you, for example, any large peaks and dips.
Start by running the target website through the Ahrefs site explorer tool, select all time, then one year, and then 30 days and look for anything which stands out to you, for example, any large peaks and dips.
If you find very large peaks which show that a website picked up too many links too quickly, this could be a sign of overly aggressive or low-quality link building which was done very fast.
It’s not always a bad thing to get a bunch of links in a short amount of time, but it must be natural. I always suggest quality over quantity.
Next, take a look at which locations the bulk of the links are coming from. If your client is operating out of one location only, for example, the United Kingdom, it will make sense to have links coming from this location.
Backlink locations
Also, look out for too many links coming from locations that you know are specifically of no interest to your client or campaign.
Anchor text analysis
A links anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. It is the words that we use to highlight and add the link to.
Every anchor text should be natural and also be relevant to the page you’re linking to.
The words contained in the anchor text helps search engines understand the context of the topic as well as how the pages fit within each other. The words contained in the anchor text will also help to determine rankings and page authority associated with the target page.
For example, if you are writing a detailed guide about healthy food for a pitbull, and a third-party website is linking to you with the anchor text ‘buy used cell phones’ then this is completely unnatural and questionable.
Ahrefs will give you a nice breakdown of your top anchors as well as the percentage of links pointing to those anchors.
When auditing, flag anchor text which is unnatural or overused. Especially exact match anchors. For example, if your client sells shoes online, you want to be on a special lookout for abundant usage of anchor text like ‘buy shoes online, or ‘shoes for sale online.
It is normal to have those types of anchors, but anything in excess is going to be an issue.
Ass the quality of backlinks pointing to the site you are auditing. There are quite a few ways of doing this and SEMrush has a unique toxic link analysis tool which is also very good for weeding out low-quality links.
However, staying in Ahrefs click on ‘referring domains’ to see what the average domain rating (DR) and traffic metrics each linking domain has so that you can filter out low-quality sites.
Ideally, you do not want more than 2 backlinks from the same domain. The very 1st link you get from a site is the most powerful in terms of link equity.
However, while you are assessing the quality of these links, if anything looks strange, click on the number arrow under the backlinks column, to reveal the backlink. From there, you can go ahead and view the page and assess it for yourself.
Locating and fixing broken links
Not only do broken pages and broken links cause a bad user experience and frustrating journey for your readers, but they will also waste ‘link juice’ aka ‘link equity.
By fixing any broken pages or broken links on your website, you will then allow the link equity to flow evenly through your website which is a crucial part of backlink optimization.
Keep your client’s site open in the site explorer, and click on ‘best by links’ underneath the pages dropdown. Then, filter for ‘404 not found’.
This will show you all of the broken pages on your website which may still have backlinks.
Sort the list by referring domains (RD) to see which broken pages have the highest amount of inbound links. Then, to restore the link equity from those pages, you will need to work through the list and decide the following:
- Is it a relevant page with a simple error that can be fixed
- Replace the content on that exact URL (the content must be within the same topic/niche)
- Permanently 301 redirect the broken page to the next most relevant page or the home page
All of these options above will allow you to regain the ‘link juice’ and equity from the backlinks pointing to those pages.
The Best SEO Audit Tools for the job
Any site audit tool will constantly be updating and being modified, the tools below are by no means the only audit tools available, but these are ones which I rely on quite a lot.
I strongly suggest staying up to date with popular search-related websites, forums, communities and think tanks such as (my personal favorite) the Traffic Think Tank. I have learned more from the Traffic Think Tank than most courses and diplomas I have completed over the years.
Many great tools are free to use and offer great value, but there isn’t a ‘quick fix’ option that promises the world – stay away from any of these.
Below is a shortlist of some audit tools to use and ones that are popular when conducting an SEO audit on a website.
Screaming Frog: One of the most advanced industry-standard website crawlers which give you the ability to access every element of your website. This includes (but is not limited to) scanning all HTML pages, images, JavaScript, CSS, metadata data as well as internal and external links.
The technical capabilities of this tool are great and have been around for a long time. Not only does Screaming Frog show you every possible aspect of On-PagePage SEO, URL structure, response codes and so much more, you can also analyze structure data all in one place and connect your Google account too. Very powerful!
Fruition: Detailed Google penalty and Google update checker. Fruition links to your Google Analytics account and checks your domain directly against every Google update, penalty update, or core algorithm change.
This tool offers great insight and excellent visual elements to help you understand any impacts on your website whether they are positive or negative. This tool should be in any SEO toolbox regardless of whether you are running SEO audits or services in general.
Ahrefs: In my opinion, one of the best backlink profile and keyword research tools ever to exist is Ahrefs. Ahrefs gives you the ability to analyze every aspect of your website’s entire backlink profile and link types. Their website auditor tool has also made great improvements over the years and has visually appealing graphics.
SEMrush: Comprehensive and full suite all in one SEO tool which has incredible site audit features, visuals, toxic link analysis, and, great content ideas. Known to be very easy to use, SEMrushes’ ability to identify toxic links and allow you to analyze them and submit them to Google for the disavow process directly from the SEMrush dashboard is really handy and easy to use.
GTmetrix: Comprehensive website speed checker and page load time testing tool. This tool offers core insights into advanced load time metrics and data both from the client-side (user) and the server-side.
Google page speed insights: Industry-standard speed testing and page load time tool which now includes core web vitals performance reports and suggestions.
Google mobile-friendly test: Excellent mobile-friendly testing tool analyzing responsiveness, mobile load time, mobile layout, and distances of buttons, images, and text. Easily identifies sites that are or are not mobile-friendly. A nice addition to this tool is that Google gives you a detailed breakdown of what is needed to improve and fix any mobile errors which show up.
Google rich snippets tool: A way to test structured data and mark-up to see if your website is eligible for rich snippets in the SERPs.
Google Analytics: The core of website reporting and measurement. Google Analytics acquires user data from each website visitor through the use of page tags.
Google Search Console: The ultimate communication tool between Google and your website allowing you to monitor site performance, index issues, view and fix page speed and page experience issues as well as to monitor for any manual or security penalties.